Subacromial syndrome
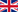
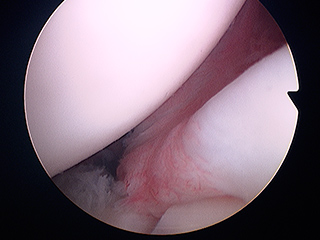
Subacromial syndrome is defined by a diminishing of space between the humeral head and the lower part of the acromion, generally due to the appearance of a bony outgrowth known as osteophyte. The decrease leads to impingement at rotator cuff level what causes shoulder pain.
Arthroscopic arthroplasty consists of removing the osteophyte (bone spur), by means of a milling cutter, which is responsible for the lessening of subacromial space.
Rotator cuff tear
Rotator cuff may tear when a shoulder trauma occurs. It can be a sudden, high stress motion or impact. But the most common cause is age-related degeneration (poor biomechanics factor). It usually happens in patients who suffer from a subacromial syndrome during an extended period. The injury Normalmente la ruptura se produce a nivel de la unión hueso-tendón. The symptons of this pathology include severe pain that radiates through the arm and limited range of motion, especially the inability to move or lift the arm sufficiently.
Arthroscopically the repair involves tissue suture. The method currently in favor is to place an anchor in the bone at the natural attachment site (humeral head) where the rotator cuff was previously anchored, and resuture the torn tendon to the anchor and fix the rotator cuff in its previous position.
Relapsing shoulder dislocation and instability
Relapsing shoulder dislocation and its instability are caused by hypermobility of the anterior shoulder capsule or by partially/totally dislocation from the socket at glenoid level (gleno-humeral joint).
Arthroscopic repair consists of re-tightening the capsule or reinserting it at glenoid level.